入职作业之 json 数据与 lua value 转换
题目任务描述:封装json格式的数据与lua value间的互相转换功能
下载ECMA-404的描述文件,观察json的数据格式。
根据描述,一个json value可以是这些类型: object, array, number, string, true, false, or null。
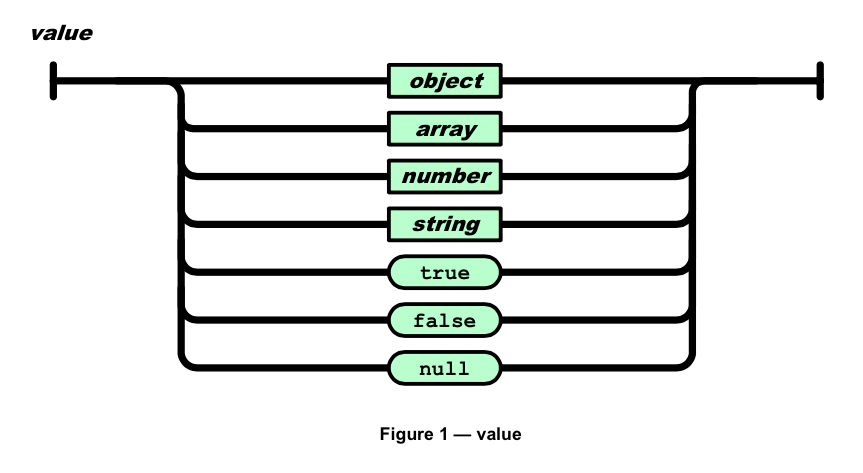
下面是描述几种数据类型的图。
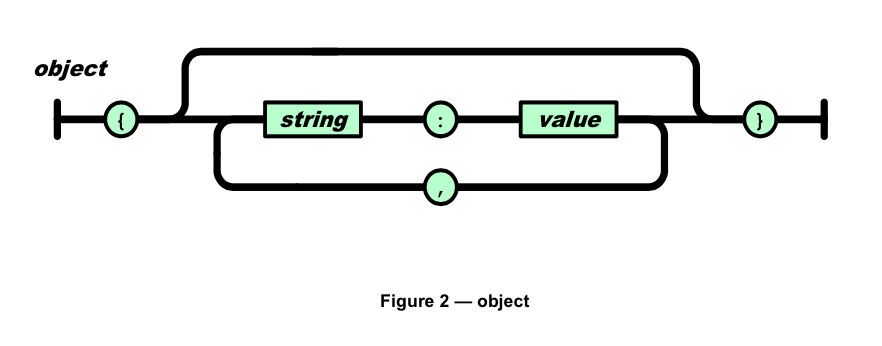
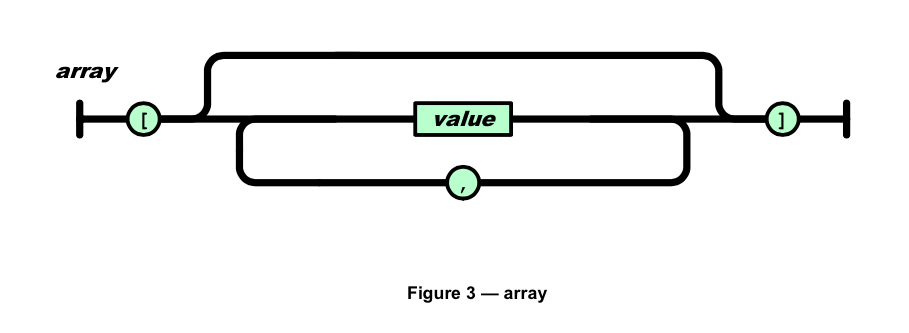
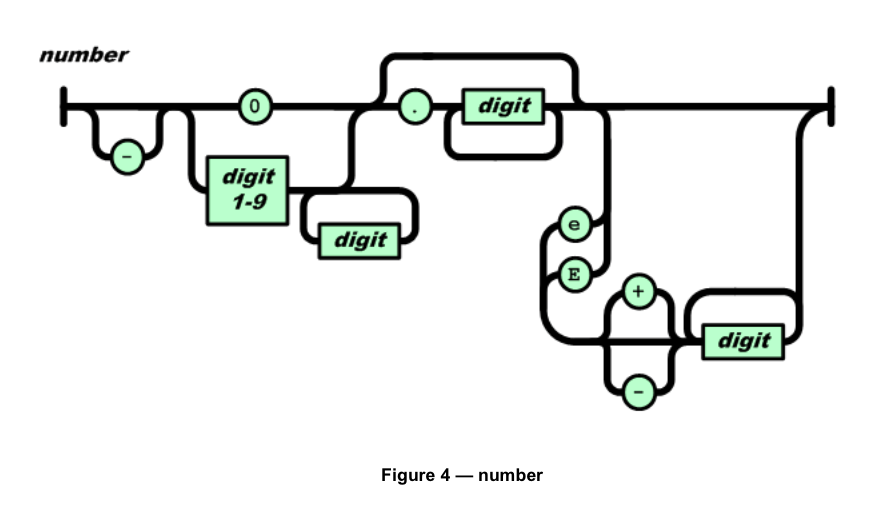
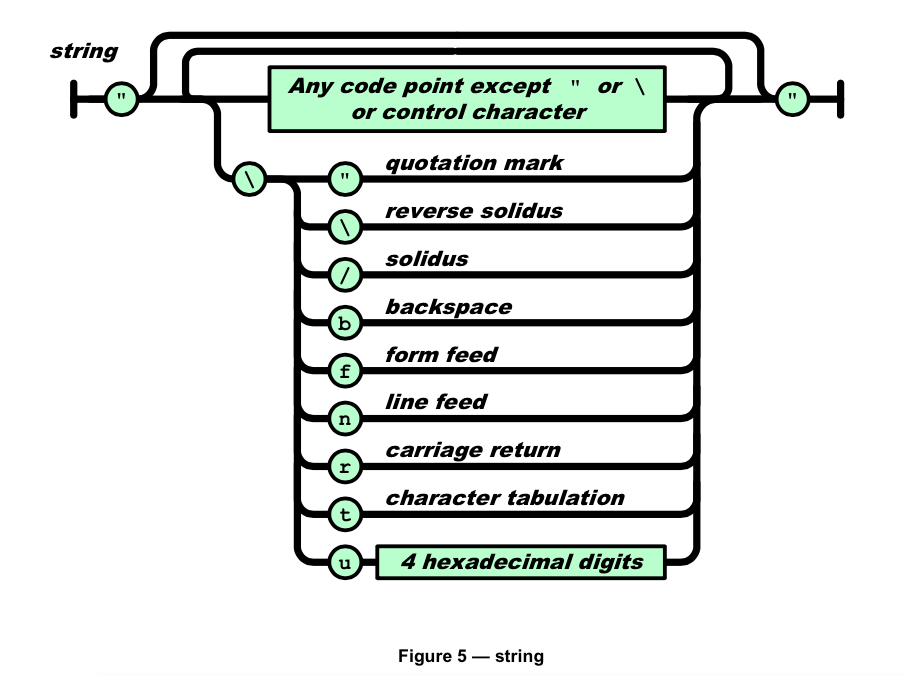
这些图的描述能力应该等同BNF,所以需要处理的操作大概有:
- 串联 如,C等于A串联B(C=AB),即匹配一个C等同于匹配一个A接着匹配一个B
-
并联 如,C等于A并联A(C=A B),即匹配一个C等同于匹配一个A或者匹配一个B -
匹配0或1次 如,C等于匹配A0或1次(C=A?),即匹配一个C等同于匹配一个A0或多次,该操作可以由 C=A ”” 代替,其中”“表示空串。 - 匹配0或任意次 如,C等于匹配A0或任意次(C=A*),即匹配一个C等同于匹配一个A0或任意次
则最简单的,上述的value可以描述成
value = object | array | number | string | true | false | null
object可以描述成,(引号内表示终结符,括号指示结合顺序)
object = "{" ((string ":" value) ("," string ":" value)*)? "}"
其他就依次类推…
回来开始写代码:
先定义最简单的匹配函数的格式:
-- the matcher function
function matcher(json_str, start)
...
return result, value, new_start
end
| 最简单的匹配函数,接受一个待匹配的字符串和一个起始下标,返回匹配结果(true | false),匹配成功后的返回数据,一个新的起始下标。 |
定义两个最简单的结果处理函数,一个不处理输入直接返回,另一个直接返回nil,后面会常用到
-- result handler
local no_h = function(v) return v end
local nil_h = function() return nil end
定义一个生成基本匹配函数的生成函数,接受一个lua find的匹配表达式和一个结果处理函数,返回一个匹配函数。
-- matcher function generator
local generator = function(pattern, handler)
– the matcher function
function matcher(json_str, start)
local _, e = string.find(json_str, "^"…pattern, start)
if e then
return true, handler(string.sub(json_str, start, e)), e+1
else
return false, nil, start
end
end
return matcher
end
根据最开始的描述,需要的操作至少还有:并联、串联、匹配0或一次、匹配0或任意次。
下面是并联多个匹配函数的并联操作,输入一个匹配函数列表和一个结果处理函数,返回一个并联后的匹配函数。
-- parallelize matchers
parallelize = function(matchers,handler)
if handler == nil then
handler = no_h
end
– the paralleized matcher function
function p_matcher(json_str, start)
local r,v,s
for i=1,#matchers do
r,v,s = matchers[i](json_str, start)
if r then
if handler == nil_h then return true, nil, s end
if handler == no_h then return true, v, s end
return r,handler(v),s
end
end
return false,nil,start
end
return p_matcher
end
下面是串联多个匹配函数的串联操作,输入一个匹配函数列表和一个结果处理函数,返回一个串联后的匹配函数。
-- serialize matchers
serialize = function(matchers,handler)
if handler == nil then
handler = no_h
end
– the serialized matcher function
function s_matcher(json_str, start)
local r,v,s = false,nil,start
local results = {}
for i=1,#matchers do
r,v,s = matchers[i](json_str, s)
if r == false then
return false,nil,start
end
table.insert(results,v)
end
if handler == nil_h then return true, nil, s end
if handler == no_h then return true, results, s end
return true,handler(results),s
end
return s_matcher
end
匹配0或任意次和匹配1或任意次之间存在转换关系,实现中选了1或任意次匹配作为原子操作,0或任意次可以描述为:(““表示空串)
0_or_more = one_or_more | ""
下面是1或任意次匹配操作,接受一个匹配函数和一个结果处理函数,返回一个匹配1次或任意次的匹配函数。
-- make a matcher match one or more
one_or_more = function(matcher, handler)
if handler == nil then
handler = function(v) return v end
end
– the one or more matcher function
function oom_matcher(json_str, start)
local r,v,s = false,nil,start
local results = {}
r,v,s = matcher(json_str, s)
if r == false then
return false,nil,s
end
table.insert(results,v)
while true do
r,v,s = matcher(json_str, s)
if r == false then
break
end
table.insert(results,v)
end
if handler == nil_h then return true, nil, s end
if handler == no_h then return true, results, s end
return true,handler(results),s
end
return oom_matcher
end
下面定义了一个空串匹配函数,和定义一个0或1次匹配操作函数。
-- empty
local empty_m = generator("",nil_h)
– or empty helper
local or_empty = function(matcher)
return parallelize{matcher,empty_m}
end
定义完这些,就可以开始描述我们的匹配函数了。
-- main matchers
local null_m, boolean_m, number_m, string_m, object_m, array_m, value_m, value_a
value匹配函数的描述,value为number_m,string_m,boolean_m,null_m,object_m,array_m并联。
-- value
value_m = function(json_str,s)
-- use value_a to bootup
if value_a==nil then
value_a = parallelize{number_m,string_m,boolean_m,null_m,object_m,array_m}
end
return value_a(json_str,s)
end
这里的value需要使用value_a来协助描述,因为代码最终会出现循环引用,此时number_m,string_m,boolean_m,null_m,object_m,array_m都还没定义,需要在定义好后,才能生成value的匹配函数。
匹配null的函数,使用生成函数生成。
-- null
null_m = generator("null",function() return nil end)
匹配boolean的函数,true和false使用生成函数生成,然后并联true和false匹配函数,生成boolean匹配函数。
-- boolean
local true_m = generator("true", function() return true end)
local false_m = generator("false", function() return false end)
boolean_m = parallelize{true_m,false_m}
匹配number的函数,根据最上面的图,描述为如下:
-- number
local sign_m = generator("[+-]?",no_h)
local minus_or_no_m = generator("[-]?",no_h)
local number_no_0_m = generator("[1-9]%d*",no_h)
local number_0_m = generator("0",no_h)
local dot_number_m = generator("%.%d+",no_h)
local e_number_m = generator("[eE][+-]?%d+",no_h)
number_m = serialize(
{
minus_or_no_m,
parallelize{number_0_m,number_no_0_m},
or_empty(dot_number_m),
or_empty(e_number_m)
},
function(t) return tonumber(table.concat(t)) end
)
string需要处理unicode2utf8编码转换及转义符号。
unicode到utf8转换函数:
-- string
local function hex2utf8(hex)
local v, utf8str = 0, ""
v = tonumber(hex,16)
if v >= 0x0800 then
utf8str = string.char(v%0x40+0x80)
v = math.modf(v/0x40)
vv = v % 0x40
utf8str = string.char(vv+0x80) .. utf8str
v = math.modf(v/0x40)
utf8str = string.char(v+0xe0) .. utf8str
elseif v >= 0x0080 then
utf8str = string.char(v%0x40+0x80)
v = math.modf(v/0x40)
utf8str = string.char(v+0xc0) .. utf8str
else
utf8str = string.char(v)
end
return utf8str
end
匹配引号的函数,使用生成函数生成。
-- string
local quotation_m = generator(""",nil_h)
匹配非”"字符的函数,生成函数生成。
local char_m = generator("[^"\]+", no_h)
转义表
local escape_char = {
["""] = """,
["\"] = "\",
["/"] = "/",
["b"] = "b",
["f"] = "f",
["n"] = "n",
["r"] = "r",
["t"] = "t",
}
匹配”"字符函数。
local backslash_m = generator("\", nil_h)
转义符号匹配和处理函数,注意传入的结果处理函数。
local escape_char_m = generator("["\/bfnrt]",function(c) return escape_char[c] end)
unicode匹配和处理函数,注意传入的结果处理函数。
local unicode_char_m = generator("u[0-9a-fA-F][0-9a-fA-F][0-9a-fA-F][0-9a-fA-F]", function(v) return hex2utf8(string.sub(v,2)) end)
string的描述
string_m = serialize(
{
quotation_m,
or_empty(
one_or_more(
parallelize{
char_m,
serialize(
{
backslash_m,
parallelize{escape_char_m,unicode_char_m}
},
table.concat
),
},
table.concat
)
),
quotation_m
},
table.concat
)
object的描述,各层结果处理函数比较复杂。
-- object
-- brace_l
local brace_l_m = generator("%s*" .. "{" .. "%s*",nil_h)
local brace_r_m = generator("%s*" .. "}" .. "%s*",nil_h)
local colon_m = generator("%s*:%s*",nil_h)
local comma_m = generator("%s*,%s*",nil_h)
local object_item_m = serialize{string_m,colon_m,value_m}
object_m = serialize(
{
brace_l_m,
or_empty(
serialize(
{
object_item_m,
or_empty(
one_or_more(
serialize(
{comma_m,object_item_m},
function(t) return t[1] end
)
)
)
},
function(t)
if t[2] then
table.insert(t[2],t[1])
return t[2]
else
return {t[1]}
end
end
)
),
brace_r_m
},
function(t)
local o = {}
if t[1] then
for k,v in pairs(t[1]) do
o[v[1]] = v[2]
end
end
return o
end
)
array的描述,array需要保持一个状态index,如果直接用基本操作描述,传入的结果处理函数会比较蛋疼,所以用函数实现了。
-- arrary
local bracket_l_m = generator("%s*%[%s*",nil_h)
local bracket_r_m = generator("%s*%]%s*",nil_h)
array_m = function(json_str, start)
local array,index = {}, 1
local add_item = function(v) array[index] = v[1]; index=index+1 end
local array_item_m = serialize({value_m},add_item)
local array_a = serialize{
bracket_l_m,
or_empty(
serialize{
array_item_m,
or_empty(
one_or_more(serialize{comma_m,array_item_m})
)
}
),
bracket_r_m
}
local r,v,s = array_a(json_str,start)
return r,array,s
end
最后,匹配函数
local function Marshal(json_str)
local result,value,start = value_m(json_str,1)
if result and start == #json_str+1 then
return value
else
return nil, "error_type"
end
end
lua table 反解析成 json string 的比较直观,对每一种lua value类型写一个转换函数即可,此处不冗述。


