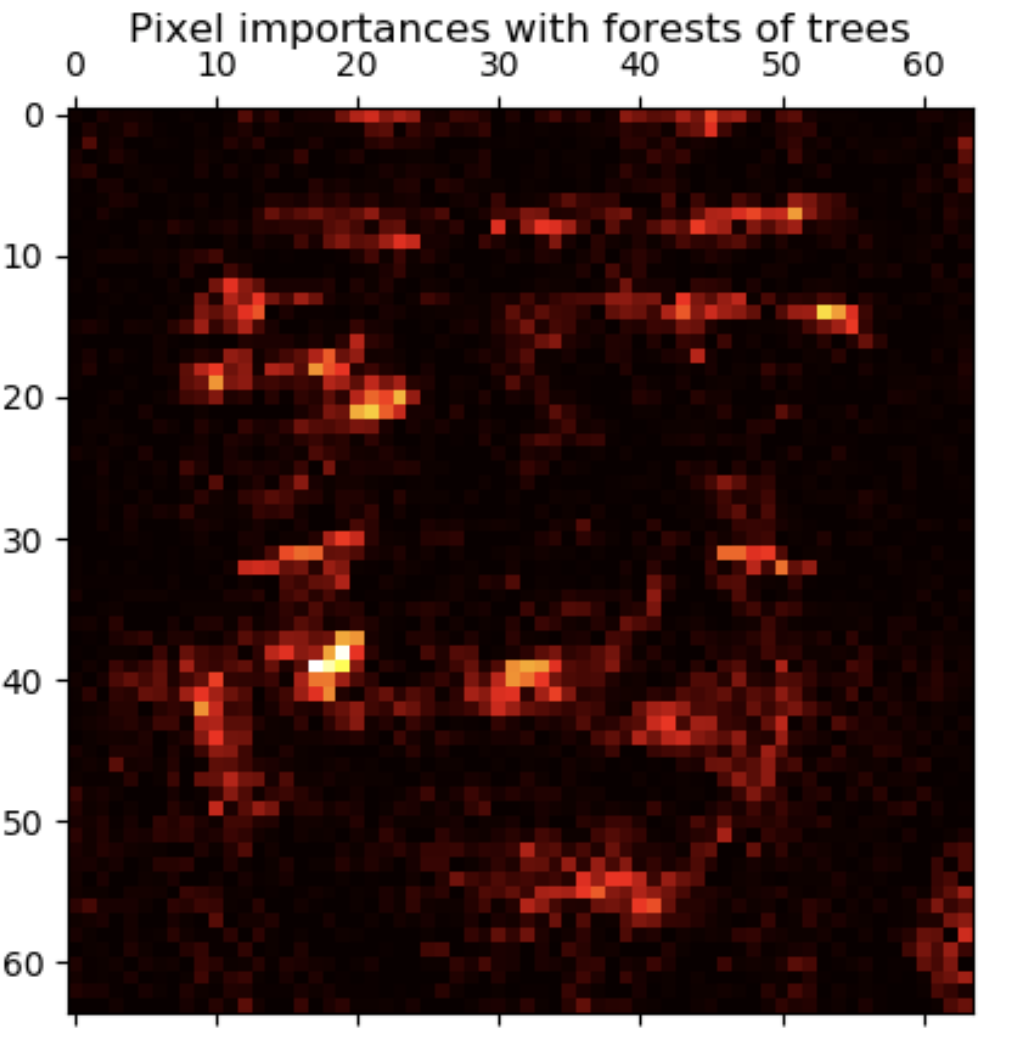
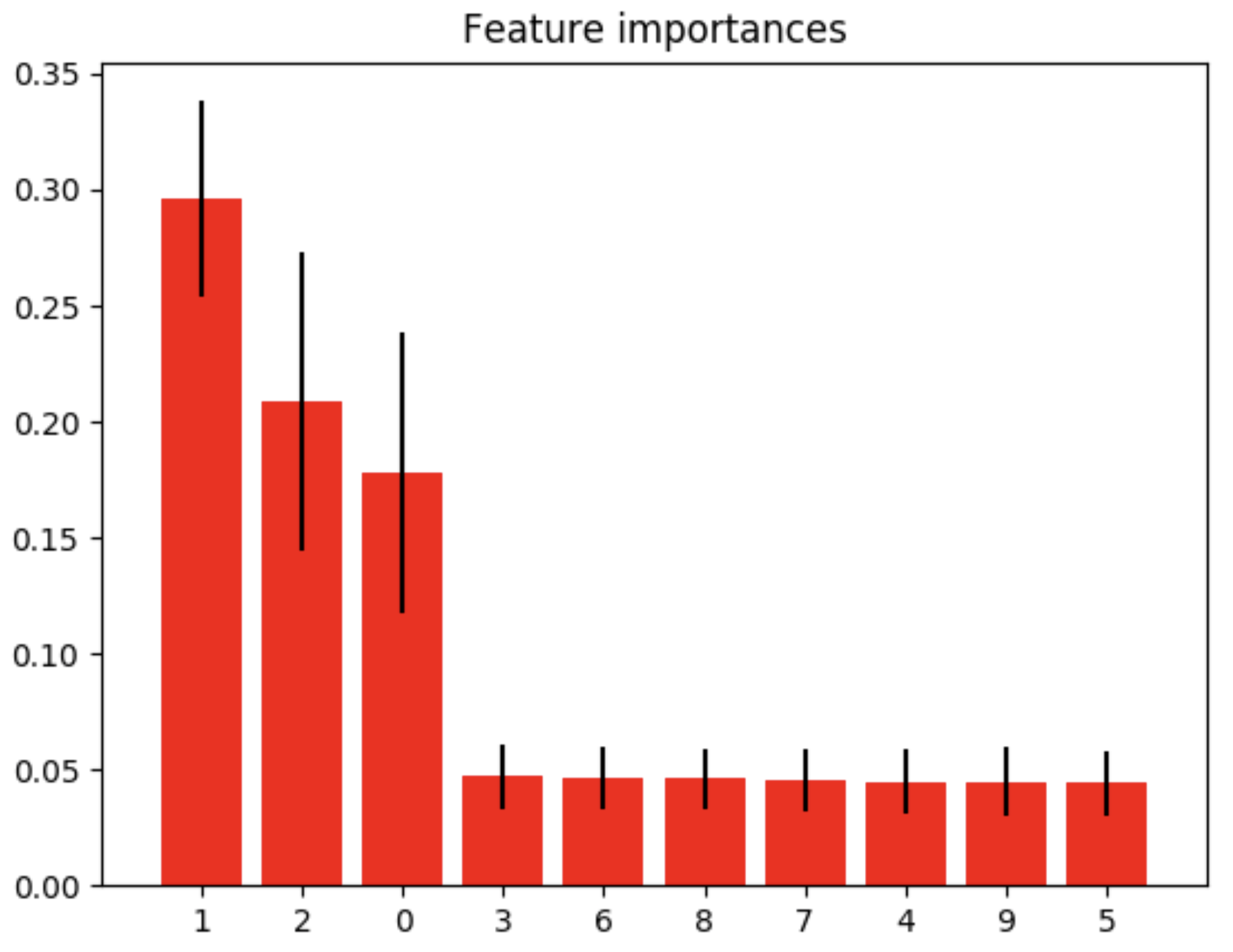
特征对目标变量预测的相对重要性,可以通过决策树中使用特征作为决策节点的相对顺序来评估。
通过对多个随机树中的预期贡献率取平均,可以减少这种估计的方差。
sklearn.ensemble模块包含两个基于随机决策树的平均算法:Random Forest 和 Extra-Tress.
实例 实例一: 特征重要性二维可视化
from time import timeimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.dataset import fetch_olivetti_facesfrom sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifiern_jobs=1 data = fetch_oliveetti_faces() X = data.images.reshape((len(data.images),-1 )) y = data.target forest = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=1000 , max_features=128 , n_jobs=n_jobs) forest.fit(X,y) importances = forest.feature_importances_ importances = importances.reshape(data.image[0 ].shape) plt.matshow(importances. cmap=plt.cm.hot) plt.title("Pixel importances with forests of trees" ) plt.show()
实例二:特征重要性一维可视化
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifierX,y = make_classification(n_samples=1000 , n_features=10 , n_informative=3 , n_classes=2 ) forest = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=250 , random_state=0 ) forest.fit(X,y) importances = forest.feature_importances_ std = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in forest.estimators_], axis=0 ) indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1 ] print("Feature ranking:" ) for f in range(X.shape[1 ]): print("%d. feature %d (%f)" % (f+1 , indices[f], importances[indices[f]])) plt.figure() plt.title("Feature importances" ) plt.bar(range(X.shape[1 ]), importances[indices], color='r' , yerr=std[indices], align='center' ) plt.xticks(range(X.shape[1 ]), indices) plt.xlim([-1 , X.shape[1 ]]) plt.show()